This procedure may help relieve pain and improve your mobility.
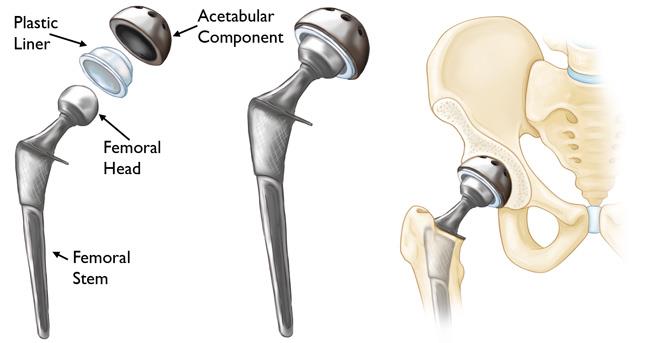
Hip replacement is a procedure in which surgeons replace a hip joint with an artificial joint.
The surgery is for people with severe hip damage, which may be caused by:
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Osteonecrosis (a disease caused by reduced blood flow to bones in the joints)
- Injury
- A chronic illness
Hip replacement can relieve pain, help you move better, and improve your quality of life.
It's an option for people who don't get enough help from more conservative treatments.
Hip Replacement Procedure
An orthopedic surgeon typically performs a hip replacement. You'll receive either general anesthesia or a spinal block.
The doctor will make an incision over the front or side of your hip and move your muscles to expose the hip joint.
Diseased and damaged bone and cartilage are removed.
Your surgeon will implant a prosthetic socket into your pelvic bone to replace the damaged one.
The top of your thighbone is replaced with a prosthetic ball that attaches to a stem.
When the procedure is complete, your doctor will reattach your muscles and close your incision.
Newer techniques allow many surgeons to perform hip replacements with a minimally invasive approach that doesn't require a large incision.
However, some research has shown mixed results in the outcomes of these procedures, compared with standard hip replacement techniques.
Before a Hip Replacement
Before having a hip replacement, you'll undergo a physical exam. You may also need an X-ray, MRI, EKG, or other imaging or lab tests.
Be sure to tell your doctor about all medicines you take before having this procedure. You may need to stop taking certain drugs, such as some NSAIDs, before your surgery.
After a Hip Replacement
You'll probably stay in the hospital for four to six days after your hip replacement surgery.
You may be given medicine to lower your risk of developing a blood clot during this time.
Your healthcare provider will probably have you start physical therapy as soon as possible. It's important that you perform all of your daily exercises during your recovery.
You'll continue having physical therapy for weeks or months after you leave the hospital. You may need to stay at a rehabilitation center for some time.
When you return home, be sure to have a friend or relative there to help.
Most people can resume normal daily activities six to eight weeks after the surgery. Complete recovery may take up to a year.
Avoid driving for eight weeks after the surgery.
Be sure to keep all follow-up visits with your doctor.
After you've healed completely, you may be able to swim, golf, hike, or ride a bike.
But you may have to avoid high-impact activities such as running. Talk to your doctor about which activities are right for you.
Risks of Hip Replacement
Potential risks of hip replacement surgery include:
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Injury to blood vessels or nerves
- Bone fracture
- Artificial hip dislocation (ball coming out of socket)
- Need for a second hip replacement
- Change in leg length
- Swelling in leg (edema)
Hip Revision
Hip replacements don't last forever.
Typically, an artificial joint will withstand 10 to 15 years of use.
After that, you may require hip revision surgery.


Editorial Sources and Fact-Checking
- Hip replacement; Mayo Clinic.
- Hip replacement; MedlinePlus.
- Questions and Answers about Hip Replacement; National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases.
- Hip Replacement; Cleveland Clinic.